By: Expert Contributor | Updated on: 2025-08-09
Super AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays have revolutionized the mobile and consumer electronics landscape, delivering an unparalleled picture quality and a truly immersive viewing experience. Unlike traditional Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) screens, which rely on backlights to illuminate pixels, Super AMOLED technology employs self-emitting organic compounds. This fundamental difference translates to superior contrast ratios, significantly deeper blacks, and far more vibrant, saturated colors, resulting in a visual leap forward that has captivated consumers and industry experts alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Super AMOLED displays, exploring their technological underpinnings, advantages over competing technologies such as LCD, standard AMOLED, and emerging contenders like MicroLED and QD-OLED, potential drawbacks, and future applications. We’ll clarify common misconceptions, address frequently asked questions (FAQs), and provide actionable insights to help you fully understand this groundbreaking display technology, regardless of your technical expertise – whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a potential buyer, or simply curious about the advancements in screen technology. This detailed exploration will cover the technical specifics of Super AMOLED, meticulously detailing its performance advantages, the practical implications for users (considering factors like power consumption, durability, and overall user experience), and offering informed comparisons to help you navigate the often confusing world of display technologies. Whether you’re choosing a new smartphone, tablet, curved gaming monitor, or other device featuring a Super AMOLED screen, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of its capabilities and limitations.

Key Takeaways
- Unrivaled Visual Fidelity: Super AMOLED displays offer dramatically superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LCDs and other AMOLED variants, resulting in a significantly more realistic and visually appealing image quality. The absence of a backlight is the key to this advantage, allowing for a true black level that LCDs simply cannot match. This results in richer colors, improved detail in dark scenes, and a more immersive viewing experience.
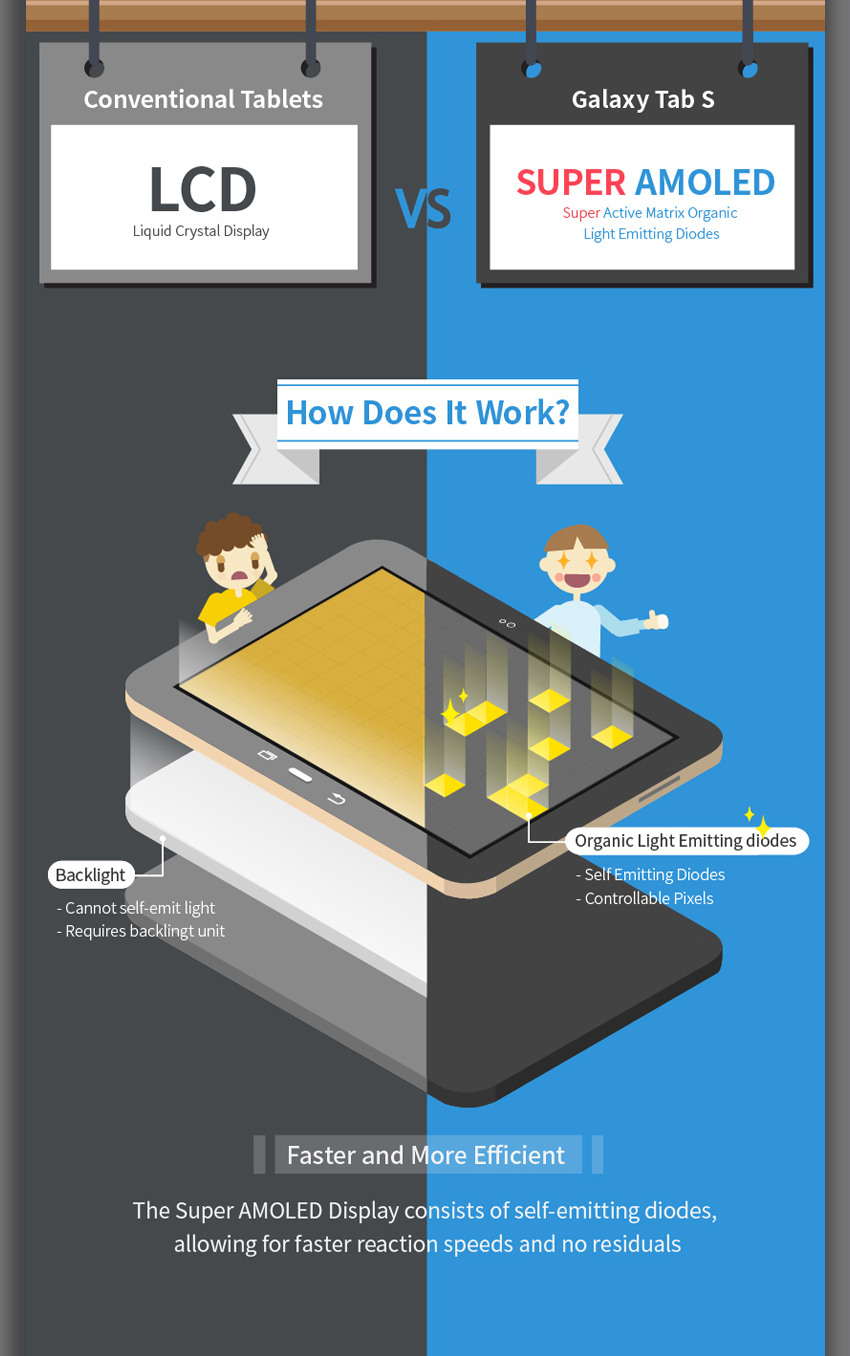
- Energy Efficiency: The self-emitting nature of Super AMOLED pixels leads to more energy-efficient performance in many scenarios, particularly when displaying content with predominantly dark areas or low brightness levels. This is because only the pixels that need to be illuminated consume power, unlike LCDs which constantly power a backlight. This contributes to extended battery life on mobile devices and reduces overall energy consumption.
- Potential Drawbacks and Mitigation Strategies: While offering significant advantages, potential downsides, including higher initial cost compared to LCD technology and the possibility of burn-in (though greatly mitigated in modern iterations), should be considered before purchasing a device with a Super AMOLED display. We will discuss strategies to minimize burn-in risk, including responsible usage habits and the advanced technologies implemented by manufacturers to combat this issue.
- Integrated Touch Sensor: Super AMOLED’s integration of the touch sensor directly onto the display panel contributes to its slimmer profile, improved responsiveness, and faster response times compared to traditional AMOLED displays which have a separate touch layer. This seamless integration enhances the overall user experience.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Super AMOLED Technology
- Super AMOLED vs. Other Display Technologies
- Addressing Common Concerns: Burn-in and Image Retention
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Understanding Super AMOLED Technology
Super AMOLED displays are fundamentally different from traditional LCDs and even other AMOLED displays. The “Active-Matrix” designation signifies the use of thin-film transistors (TFTs). These TFTs act as tiny, individually controlled switches, regulating the electrical current flowing to each pixel. This precise control enables faster response times, resulting in smoother animations and more accurate image reproduction, especially crucial for fast-paced gaming or video content. This precision also allows for higher resolutions, packing more pixels into a smaller space, leading to sharper and more detailed images. The higher pixel density delivers a crisper and more refined visual experience, significantly enhancing the viewing pleasure. The increased pixel density also allows for better scaling of images and videos, preventing pixelation or blurring that can occur on displays with lower resolutions.
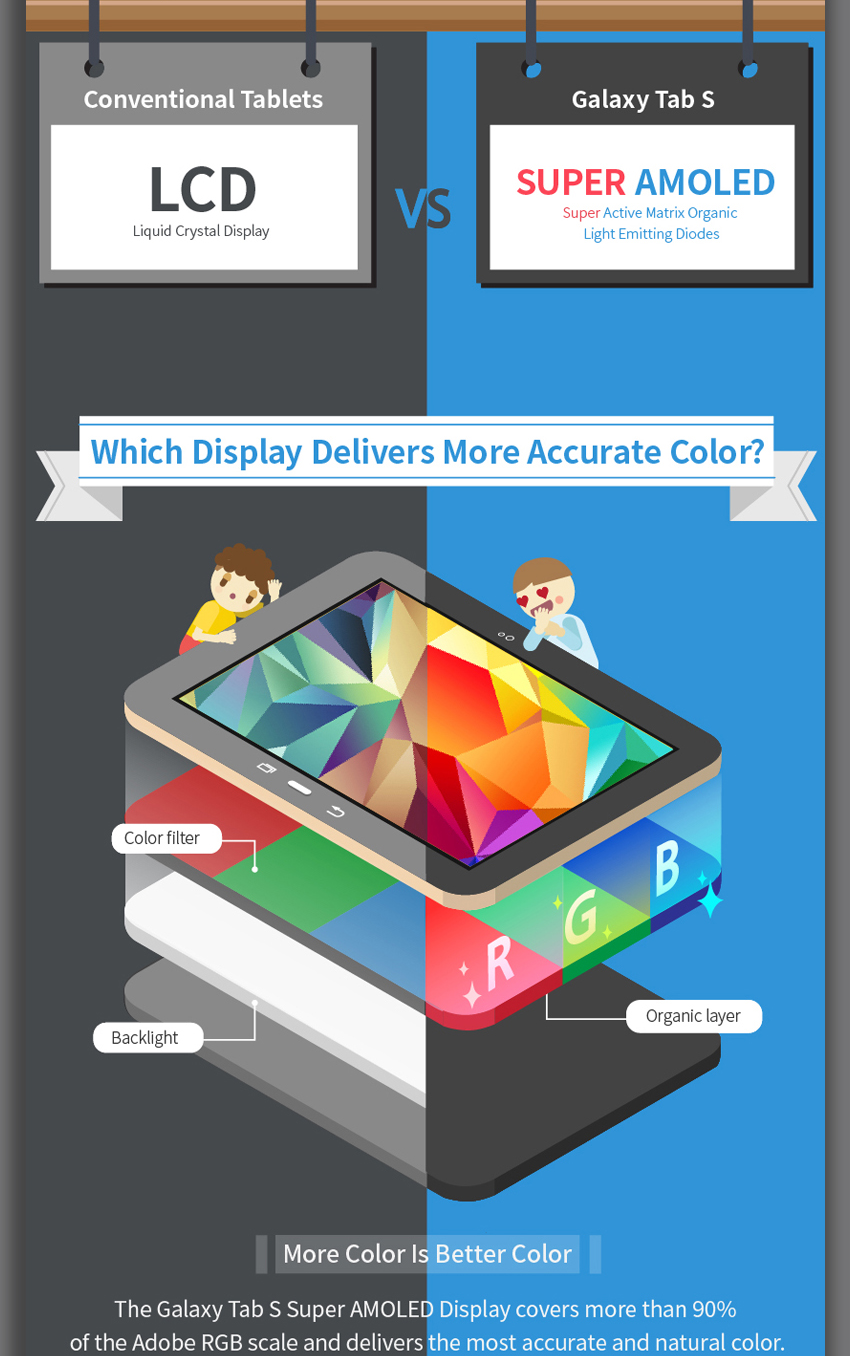
The “Organic Light-Emitting Diode” (OLED) component refers to the self-emitting organic compounds. These organic materials generate light when an electrical current passes through them. This direct light emission is the cornerstone of AMOLED technology’s superiority over LCD technology. LCDs, in contrast, utilize a backlight to illuminate liquid crystals, which then either block or allow light to pass through to create the image. This backlight is a significant power consumer and severely limits the depth of blacks achievable in LCD displays. Because each pixel in a Super AMOLED display produces its own light, true blacks are possible, leading to incredibly high contrast ratios (often exceeding 100,000:1), dramatically improved energy efficiency, and exceptional image clarity. The absence of a backlight also allows for a significantly slimmer profile, a key factor in the sleek designs of many modern mobile devices.
“The self-emitting nature of Super AMOLED pixels eliminates the need for a backlight, a key factor contributing to its superior contrast ratio, increased energy efficiency, thinner form factor, and vibrant color reproduction.”
The manufacturing process of a Super AMOLED display involves depositing meticulously patterned layers of organic materials onto a substrate, usually glass. These layers form individual pixels, each controlled by an integrated TFT. This intricate process, involving precise deposition and patterning techniques, contributes to the higher cost of Super AMOLED displays compared to LCDs. The precision required in the manufacturing process necessitates advanced fabrication techniques and specialized equipment, resulting in higher production costs which are reflected in the final product price.
Super AMOLED vs. Other Display Technologies
The advantages of Super AMOLED become strikingly apparent when compared to other display technologies. Compared to traditional LCDs, Super AMOLED boasts vastly superior contrast ratios, resulting in deeper blacks and more vibrant, truer-to-life colors. The response times are significantly faster, resulting in smoother motion, reduced motion blur, and virtually eliminating ghosting effects often seen in LCDs. LCDs also struggle to reproduce accurate colors, particularly in darker scenes, whereas Super AMOLED offers a wide color gamut, encompassing a larger portion of the visible color spectrum (often exceeding 90% of the DCI-P3 color space), resulting in more realistic and visually stunning imagery. This wide color gamut allows for more accurate and vibrant color representation, improving the overall viewing experience.
Other AMOLED technologies exist, such as standard AMOLED and OLED. Super AMOLED often incorporates additional features and optimizations to further enhance performance. For instance, Super AMOLED frequently integrates the touch sensor directly into the display panel. This eliminates the need for a separate touch layer, leading to a slimmer display, improved touch responsiveness, and faster touch response times. Standard AMOLED displays typically have a separate touch sensor layer, adding to the overall thickness and potentially introducing minor latency. This difference in design significantly impacts the overall user experience.
OLED technology, while similar to AMOLED, may differ in the specific materials used and manufacturing processes. While both produce self-emitting light, subtle differences in color reproduction, efficiency, and lifespan can exist. These differences, while often subtle to the average user, can be significant for professionals or those with keen eyes for detail.
Choosing between Super AMOLED and other display technologies depends on several factors including budget, desired performance characteristics, screen size, power consumption requirements, and the specific application. Higher-end smartphones, premium tablets, and high-performance gaming monitors often leverage Super AMOLED for its superior image quality and performance, while more budget-friendly options may opt for LCD or standard AMOLED to reduce manufacturing costs. Understanding the nuances of each technology empowers consumers to make informed decisions.

💡 Pro Tip: When comparing displays, scrutinize specifications such as contrast ratio (higher is better), response time (lower is better), color gamut coverage (wider is better, often expressed as DCI-P3 or Adobe RGB coverage), peak brightness (measured in nits), and resolution (higher is better, measured in pixels per inch or PPI). These metrics provide a quantitative assessment of image quality and performance, allowing for a more objective comparison between competing display technologies.
Addressing Common Concerns: Burn-in and Image Retention
One frequent concern associated with AMOLED displays, including Super AMOLED, is burn-in, the permanent discoloration or ghosting of an image on the screen. This phenomenon occurs when pixels are subjected to prolonged exposure to static content. However, modern Super AMOLED displays employ sophisticated algorithms and hardware to actively mitigate the risk of burn-in. These techniques include pixel shifting, which dynamically adjusts the position of the displayed pixels, and automatic dimming of static elements. While burn-in remains a theoretical possibility with extreme and prolonged exposure to static content, it’s far less likely than it was with earlier AMOLED technology. Manufacturers have invested significantly in burn-in prevention strategies, making it a considerably less significant concern for the average user. Responsible use, avoiding prolonged display of static content such as unchanging widgets, navigation bars, or constantly-displayed logos, further minimizes the risk. The advanced algorithms and hardware are continuously being improved, ensuring that future Super AMOLED displays will be even more resilient to burn-in.
Image retention is a related concern, where a faint afterimage of a previously displayed image might linger temporarily. This is distinct from burn-in, which is permanent. Image retention is generally temporary and dissipates quickly. Unlike burn-in, which represents a permanent change in the physical structure of the pixels, image retention is a temporary effect on the organic materials and typically resolves itself automatically without any user intervention. This temporary effect is often unnoticed by most users.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between AMOLED and Super AMOLED?
The primary difference lies in the integration of the touch sensor. Both AMOLED and Super AMOLED utilize self-emitting organic LEDs, but Super AMOLED integrates the touch sensor directly into the display panel itself. This results in a thinner, more energy-efficient, and slightly more responsive display. In traditional AMOLED screens, the touch sensor is a separate layer, adding to the overall thickness and potentially introducing minor latency. The integrated touch sensor in Super AMOLED contributes significantly to its superior performance, sleek design, and improved overall user experience. This seemingly small difference in design and manufacturing leads to tangible improvements in usability and aesthetics.
Conclusion
Super AMOLED technology represents a significant leap forward in display technology, offering demonstrably superior image quality and performance compared to traditional LCDs and other AMOLED variants. Its vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios create an immersive and visually engaging viewing experience, making it a highly sought-after feature in high-end smartphones, tablets, curved gaming monitors, and other consumer electronics. While the higher initial cost and the theoretical possibility of burn-in (though highly unlikely with modern technology and responsible usage) should be considered, the advantages frequently outweigh these concerns for most users. Understanding the nuances of Super AMOLED empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions and appreciate the technological advancements it brings to the world of vibrant and immersive display experiences. The ongoing refinement and development in Super AMOLED technology promise even more stunning and energy-efficient displays in the future.